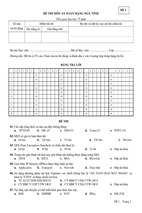
Mô tả:
DSL
Chapter 6
Digital Subscriber Line
(DSL)
Korea-Vietnam Friendship IT College
DSL
Overview
•
•
•
•
Introduction
DSL Technology and standards
Asymmetric DSL
Symmetric DSL
2
Korea-Vietnam Friendship IT College
DSL
Introduction
• xDSL is the term for the Broadband Access technologies
based on Digital Subscriber Line (DSL) technology
– “x” signifies that there are various flavors of DSL
• Provides always-on, high-speed data services over
existing copper wires to residences & businesses
– POTS service and DSL coexist on same copper line
• Lower rate xDSL (up to 1.5 Mbps) is gaining popularity
in the residential market; will get faster and cheaper
• High performance xDSL (up to 52 Mbps) targets
business and high-end users
3
Korea-Vietnam Friendship IT College
DSL
Introduction
Benefits
• High-speed data service
Application
• High speed Internet
access
• SOHO
• Multimedia, Long
distance learning, gaming
• Video on Demand
• VPN
• VoDSL
- DSL typically >10x faster than
56-kbps analog modem
• Always on connection
– No need to “dial-up”
• Uses existing copper wires
– Co-exists w/ POTS service
• Reasonably priced today
and getting cheaper
4
Korea-Vietnam Friendship IT College
DSL
DSL Technology
• Convert traditional telephone twisted-pair copper wires
to broadband communication media
• Utilize the spectrum unused by voice transmissions.
5
Korea-Vietnam Friendship IT College
DSL
DSL technology
• Digital data are sent in packets composed of digital
bitstreams in the spectrum above the 3.4 kHz (Kilohertz)
RF (Radio Frequency) band. Voice conversations occupy
the spectrum between the 300 Hz and the 3.4 kHz RF
frequencies.
6
Korea-Vietnam Friendship IT College
DSL
DSL network configuration
7
Korea-Vietnam Friendship IT College
DSL
DSL Standards
• ANSI
• ETSI
• ITU:
• ITU-T G.992.1 Recommendation supports utilization of a filter for splitting data
from voiceband signals.
• ITU-T G.996 Recommendation defines methods and procedures for
benchmarking performance and interoperability of DSL transceivers.
• The ITU-T G.997.1 Recommendation describes DSL functions in using SNMP
(Simple Network Management Protocol) and DSL Physical Layer or Layer 1
operations.
• DSL FORUM
• DLNA
• UPnP
8
Korea-Vietnam Friendship IT College
DSL
Asymmetric DSL (ADSL)
• “Asymmetric” => faster downstream rate vs. upstream
– Suitable for applications such as web-browsing, MP3
downloading, Video on demand (VoD)
9
Korea-Vietnam Friendship IT College
DSL
Asymmetric DSL (ADSL)
• Types of asymmetric DSL
– Asymmetric DSL (ADSL)
• The original and most popular
• Other asymmetric DSL technologies derived from ADSL
– Universal ADSL (UDSL), a.k.a. G.Lite or DSL Lite
• Expedites and reduces cost of deployment process by
moving the splitting process from the CP to the CO
• Splitter-less nature slows the bit rate considerably
10
Korea-Vietnam Friendship IT College
DSL
Asymmetric DSL (ADSL)
– Rate-Adaptive DSL (RADSL)
• Detects highest possible line rate & adjusts accordingly
– Very High Bit-rate DSL (VDSL)
• Used to get high speed over short local loops
• Typically used in conjunction with Fiber to the Curb
(FTTC)
• Still in development phase
11
Korea-Vietnam Friendship IT College
DSL
Symmetric DSL (SDSL)
• “Symmetric” => downstream & upstream rates are equal
– Suitable for office type apps like Video conferencing
• Types of symmetric xDSL
– Symmetric DSL (SDSL)
• Based on HDSL but single pair
• Spectral compatibility an issue (crosstalk & interference)
– High bit-rate DSL (HDSL)
• The first of the symmetric DSL technologies
• Uses multiple wire pairs (2 or 3) to achieve high bit rates
12
Korea-Vietnam Friendship IT College
DSL
Symmetric DSL (SDSL)
– HDSL 2
• Single-pair version of HDSL
• More standards driven to improve interoperability and spectrally
compatible with other loop services (ISDN, T1, HDSL)
• Takes into consideration diminishing amount of copper pairs
– Single-pair HDSL (SHDSL)
• Similar to HDSL 2, but more generalized
• Business class DSL for transporting T1/E1, ISDN, ATM, and IP
– ISDN DSL (ISDL)
• DSL over ISDN; okay to pass through repeaters & DLCs
• Always-on, flat rate billing, and transmit data over data network
13
Korea-Vietnam Friendship IT College
DSL
DSL Technologies
14
Korea-Vietnam Friendship IT College
DSL
DSL Equipments
Two groups of equipment
• Central Office - DSL Access Multiplexer (DSLAM), Repeaters
• Customer Premise - DSL Modems, Gateways, Network
Interface Card (NIC), splitters and filters
15
Korea-Vietnam Friendship IT College
DSL
DSLAM
• DSLAM is usually found in a Central Office
• xDSL line cards are installed in a DSLAM to terminate
incoming xDSL signals
• The DSLAM then combines multiple xDSL access lines
into one high speed line
• The muxed traffic is converted into ATM cells which gets
sent over an ATM backbone
16
Korea-Vietnam Friendship IT College
DSL
DSL Modem/Gateway
• A xDSL modem is the device found at the customer’s
premise which is used to transmit & receive xDSL
signals
• Could be an external “box” or a network interface card
placed inside a computer
• An xDSL Gateway combines the functionality of a
modem and router
17
Korea-Vietnam Friendship IT College
DSL
ADSL Modem Structure
Mbit/s
kbit/s
Mbit/s
ADSL
Modem
ADSL
Modem
Line
POTS
Filter
POTS
Linecard
kbit/s
POTS
Filter
Exchange End
Customer End
18
Korea-Vietnam Friendship IT College
DSL
Summary
19
Korea-Vietnam Friendship IT College
- Xem thêm -